What is food intolerance?
According to NHS ‘’a food Intolerance is difficulty digesting certain foods and having an unpleasant physical reaction to them.
It causes symptoms, such as bloating and tummy pain, which usually happen a few hours after eating the food’’.
Food intolerances do not involve an immediate response.
There is a delay in symptoms that can take from 45 minutes to several days for them to become apparent.
Medical name for FOOD INTOLERANCES is “Non-IgE mediated food hypersensitivity”, which is sometimes loosely referred to as “food hypersensitivity”.
This is also known as a “Type III Allergy” and is IgG-mediated.
It is characterised by the production of IgG antibodies and the gradual formation of antigen/antibody complexes.
Although, these are deposited in tissues, which cause chronic inflammation.
The mechanism of food intolerance involves the production of antigen/antibody complexes which are deposited in the tissues.
This triggering the release of inflammatory chemicals causing damage and inflammation in that particular tissue and this could be in any part of the body.
The best example of food intolerance is lactose intolerance.
This condition is characterized by:
- bloating
- loose stools
- diarrhoea
- gas
Lactose intolerance is caused by an inability of the body to produce enough of the enzyme lactase, which breaks down lactose, the primary sugar found in milk.
Avoiding milk products or supplementing the diet with lactase enzyme is the best way for a person with lactose intolerance to overcome the problem.
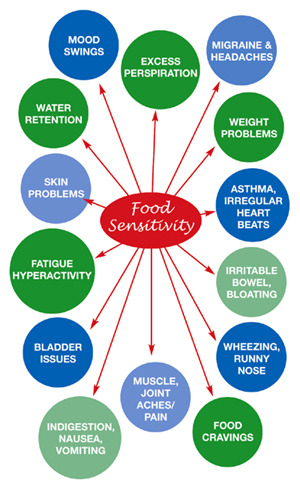
What are the sighs and symptoms?
Food intolerance symptoms usually begin about half an hour after eating or drinking the food in question, but sometimes symptoms may be delayed by up to 48 hours.
People who have a food intolerance tend to experience:
- Headaches
- Migraines
- Fatigue
- Urticaria
- Functional dyspepsia
- Asthma
- Skin disorders (rashes, angioderma, dermatitis, eczema)
- Sinusitis
- Cough
- Mouth ulcers
- Abdominal cramps
- Nausea
- Gas
- Constipation (Chronic)
- Intermittent Diarrhoea
- Irritable bowel syndrome
According to research, food intolerance has been associated with irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel diseases such as Crohn’s disease.
What is the difference between food allergy and food intolerance?
The food is extremely important to health and the body can react to certain foods in a negative way, causing the body to have an inflammatory reaction.
There are two levels of reactions, food allergy and food intolerance.
Food allergy can be an abnormal immune system response, which can cause anaphylactic shock and difficulty breathing.
Food intolerance is an adverse reaction to a food that does not involve the immune system and the reactions can be immediate or delayed up to 20 hours after a food is eaten.
Is there a test which can determine food intolerances?
There are no medical tests that can be identified or established to provide an accurate view of particular food types that a person may have an intolerance to.
Usually, people advised to take a food diary and to note any symptoms they may experience after consuming any types of food.
This would provide them an overview of foods they may have an intolerance to.
Unfortunately, this method takes time and may not be very accurate.
Bioresonance therapy can provide a more effective and accurate method of testing for food intolerances.
It is possible to test for over 200 foods in less than 30 minutes.
The accuracy is around 85% and is an efficient and cost-effective way of testing for this critical health parameter.
You can read also about: Detoxification: The secret of 21st century